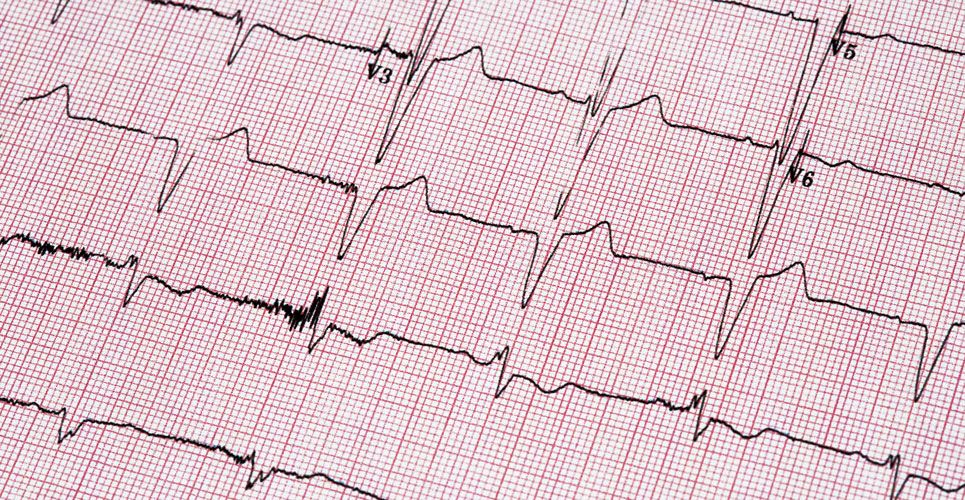
Atrial fibrillation (AF) appears linked with several cerebrovascular pathologies including strokes, lacunes and silent brain infarcts.
Atrial fibrillation (AF) is the most common arrhythmia diagnosed in clinical practice and according to one international database, in 2017 there were 3.046 million new cases registered. The condition increases the risk of stroke and thus cognitive impairment but one study also showed that AF is associated with an almost three-fold increased risk of dementia. Moreover, there is a growing body of literature that supports AF as being a risk factor for both cognitive decline and dementia although the mechanisms responsible for this association are diverse and not solely related to the increased risk of stroke.
In trying to understand the associations a team from the Institute of Neuroscience and Physiology, Sahlgrenska, Gothenburg, Sweden, set out to determine whether AF was associated with cerebrovascular pathologies. The team obtained data from the Gothenburg H70 Birth Cohort Studies, which included individuals born in 1944 who underwent structural brain MRI scans between 2014 – 2017. Using these scans, the team looked for markers of cerebral small vessel disease such as white matter hyper-intensities (WMHs), lacunes, brain infarcts and cerebral micro-bleeds, with the latter two conditions assessed by a radiologist. The patient’s diagnosis of AF was either self-reported or based on electrocardiogram results or data from Sweden’s National Patient Register (NPR). A control group of patients who did not undergo an MRI scan were included for comparative purposes.
Findings
A total of 776 participants were included of whom 65 (8.4%) had a diagnosis of AF. The presence of AF was associated with a history of symptomatic stroke (odds ratio, OR = 4.5 95% CI 2.1–9.5), large infarcts (OR = 5.0), lacunes (OR = 2.7) and silent brain infarcts (OR = 3.5). Additionally, individuals with AF had larger WMH volumes than controls, especially those currently treated for AF.
The authors concluded that AF was associated with broad range of cerebrovascular pathologies and called for further work to establish whether cerebrovascular MRI markers could help to complement current treatment guidelines for patients with AF.
Citation
Ryden L et al. Atrial Fibrillation, Stroke, and Silent Cerebrovascular Disease: A Population-Based MRI Study. Neurology 2021